You must have administrator rights to access this feature.
Automations are automated actions created in Automation Manager. An Automation includes a trigger and one or more actions. A trigger is the cause and the action is the effect.
Actions that can be automated include:
- Send an email notification
- Create records
- Edit existing records
- Verify a field value and display an error message if necessary
- Perform a calculation and set a field value
Automation Triggers
A trigger is what causes the action to occur. The system comes with 200+ triggers. Some are basic with just a specific trigger, and others are guided, with actions already associated to them.
A basic trigger is available for every parent-level recordset and child-level recordset, including custom versions.
Some triggers include configurable fields. For example, the trigger “After an Asset Type inspection is created” requires you to select the Asset Type for the trigger. Properties can also be set on triggers. The same trigger can be used in various Automations and may be configured in a number of ways.
Guided triggers include actions already associated to them. The system includes guided triggers for common situations where an Automation would be valuable. The following triggers are guided:
- Assign a task with a specific activity when it is created
- Close a work order when all related tasks are complete
- If a request is overdue send a notification
- If a task is overdue change its priority and send a notification
- If an Automation fails send a notification
- If an open task’s due date is before today, update its priority to High and send a notification
- Notify the fleet shop prior to the next vehicle PM task
- Notify when a task is completed with no cost
- Notify when a task’s costs are too high
- Notify when request with a specific issue is created
- Repeat a task 30 days after completion
- Require usage when completing equipment tasks
- Set a work order priority equal to the highest priority associated open task
- When a work order’s cost exceeds a certain amount send a notification
You know the trigger is guided if:
- The name does not start with:
- Create or edit
- Send a notification
- Verify or perform
- After selecting a trigger, actions blocks are already included in the Automation.
There are three types of triggers:
- Event-based
- Scheduled
- Manual
Event-based triggers are kicked off when the described event occurs in the system. Event-based triggers begin with the key word Create, Send, or Verify and contain the word after or before to describe the timing of when the trigger fires. It is important to appropriately align the timing of a trigger and the corresponding action or actions.
| TRIGGER TIMING | CORRESPONDING ACTION |
| Before a record is saved |
|
| After a record is created or edited |
|
Scheduled triggers are kicked off based on the defined schedule. Specify the day and time when the trigger should fire, and the system automatically kicks it off. Scheduled triggers are used to automate actions based on the passage of time—for example, sending an email notification when a task is overdue.
Manual triggers are kicked off when a user clicks the Run Now button in Automation Manager. Manual triggers are used to create or edit records in bulk. The Automation defines which records should be created or edited and what their values should be.
Scheduled Triggers in Automations
These options are available for Time-Based Triggers:
- Daily is set time of day to run
- Weekly is set which days of the week and what time of day to run
- Monthly is which days of the month and what time of day to run
- Yearly is which months and what time of day to run. This trigger runs the first of the month.
Usage:
- Includes option to Run Now to manually run an automation that is scheduled for a different time.
- When defining the schedule, note other scheduled processes that may be running and schedule during times when less users are in the system.
Manual Triggers in Automations
Manual Triggers are kicked off when a user clicks the Run Now button in Automation Manager. Manual triggers are used to create or edit records in bulk. The Automation defines which records should be created or edited and what their values should be.
In some cases, a user might have an Automation that they want to fire on command. Setting up a Manual Trigger helps solve these scenarios.
Usage:
- Typically used for one-time or infrequent events.
- Used for multi-edit functionality to edit many records at once.
For example, set all pavement segments where Street is Highway 20 to a pavement classification of asphalt.
- All manual automations are expected to complete in 2 minutes or less. To determine if the automation successfully completed, access the Automation Log.
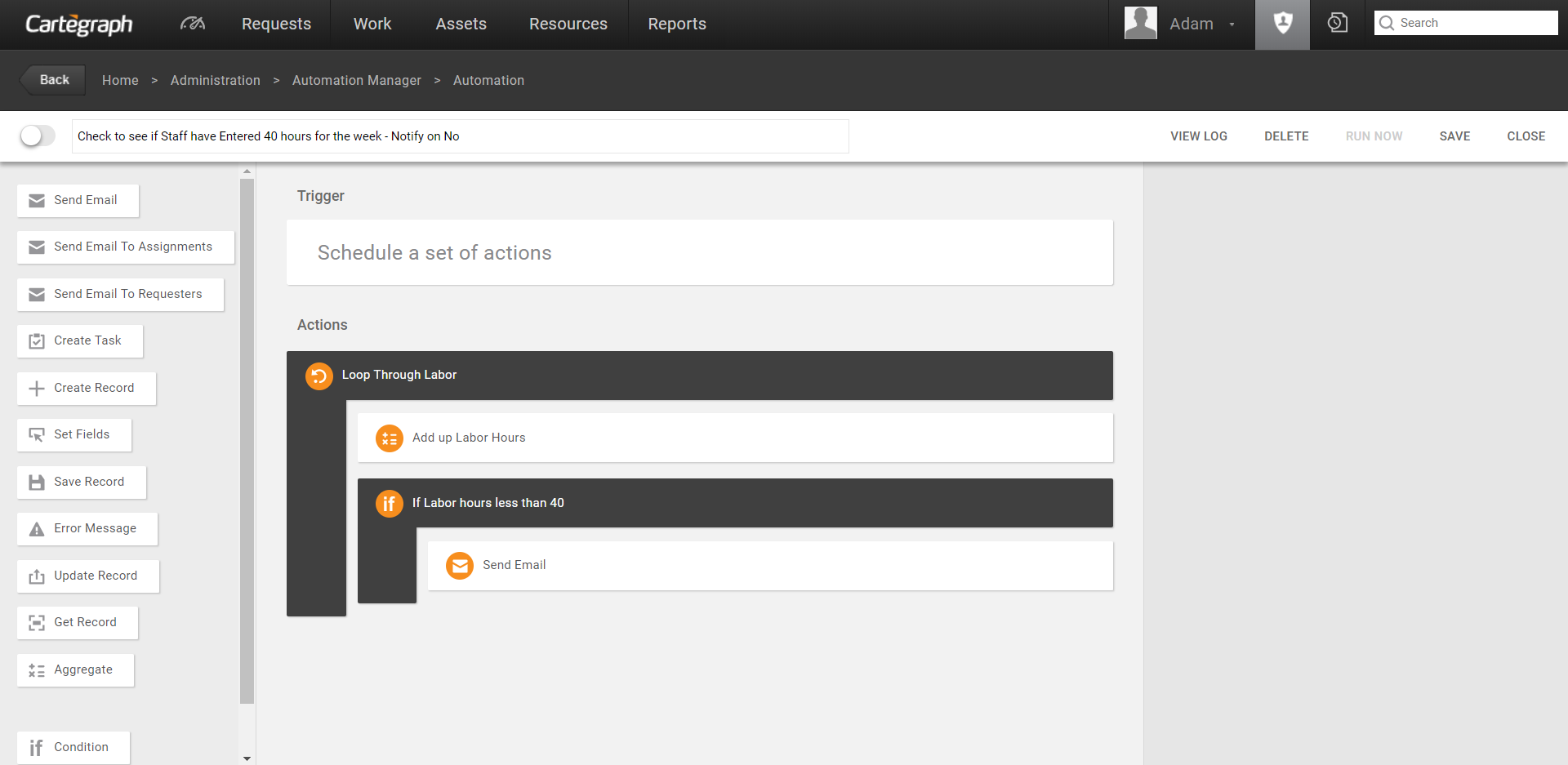
Automation Actions
Actions are what the Automation does once the trigger fires. Actions can be simple to complex, but all are made of blocks with defined properties. In the interface, when building an Automation there are three panels.
- The left panel contains all the blocks.
- The middle panel contains the selected trigger and is the workspace where blocks are placed to build the actions.
- The right panel displays the properties of the selected item in the workspace. This is where you define what the block does.
There are two types of blocks: action and support.
Action blocks cause an action to take place in the system once a trigger is fired. Action blocks include:
- Send Email
- Send Email to Assignments
- Send Email to Requester
- Create Task
- Create Record
- Set Fields
- Save Record
- Error Message
- Update Record
Support blocks provide assistance in achieving the desired action. They may be used to retrieve records, calculate values, and include conditional logic. Support blocks include:
- Get Record
- Aggregate
- Condition
- Loop Records
User Interface
- Analytics Dashboard
- Navigation Persistence
- Global Search
- Table of Contents/ Layers
- Map Tools
- Documents Attachments
- List View Data Export
- More Information…
Request Management
Work Management
- Work Orders
- Repeating Work Orders
- Tasks
- Activities
- Task Calendar
- Time Sheets
- Distribute Resources
- Task Triggers
- Preventative Maintenance
- More Information…
Asset Management & Analytics
Resource & Inventory Management
Report Management
Mobile Management
- Cartegraph for iPad and Cartegraph One Feature Comparison
- Cartegraph for iPad
- Cartegraph One
- More Information…
Workflow Management
System Management
- Structure Manager
- Library Manager
- Layout Manager
- Esri and Active Directory
- Security Role Administration
- System Licensing
- System Requirements
- More Information…
